# Authentication Methods
Updated: 30 September 2025
Authentication (Listed in Order of Preference)
# Modern Authentication
This is the new, recommended method for authentication.
It requires an Azure Application Registration (Please refer to the document Enable Modern Authentication in DMSforLegal, DMSforSharePoint and DMSforOffice. This new method utilizes Microsoft's best practics for authentication and security using the 'Microsoft Authentication Library' (MSAL). Once the application is properly registered, the following information will be required:
- Application ID
- User name (UPN) (Email address for user.)
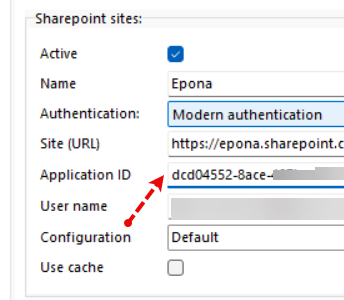
The user name is saved after initial login if the user name is not pre-defined either by the user or the deployment scripts.
Succesfully authenticating with Modern Authentication will write a file called .msalcache.bin in the %APPDATA%\Roaming\Epona\DMSforLegal (product name)\Cache folder
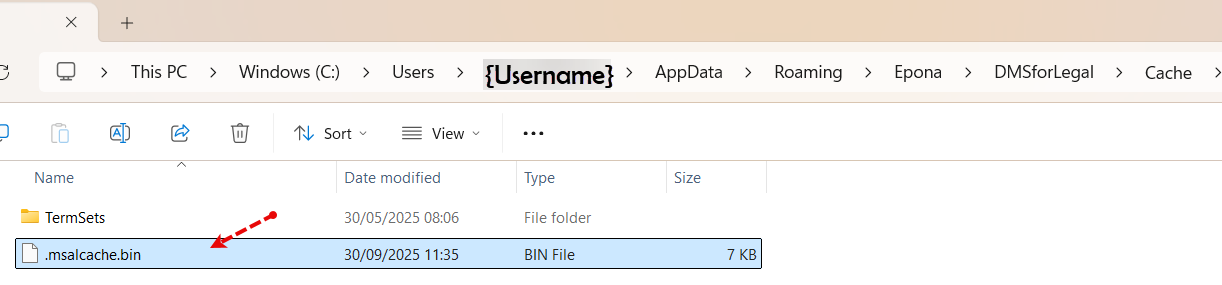
The file .msalcache.bin is the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) token cache. It’s intentionally protected by the OS (DPAPI on Windows) so it cannot be decrypted outside the original user/machine context.
If you remove the msalcache.bin file, a re-authentication requestion would trigger the user to provide login information and the MSAL library would write a new msalcache.bin file to %APPDATA%. All users can access the %APPDATA% location, you do not need to be a local administrator.
Remark: DMSforLegal (DMSforSharePoint, DMSforOffice) version 25.2, 25.3 and above require the .Net framework installed on the Windows computer to be at least version 8.0.14 (or higher). For information on the .Net version installed, please check https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/core/install/how-to-detect-installed-versions?pivots=os-windows (opens new window)
# Browser Authentication
This authentication method can be used when Modern Authentication is not available.
Browser authentication can be used when multi-factor authentication (MFA) is enabled for users. Of course Modern Authentication also supports multi-factor authentication. There is no requirement for the Username and Password to be entered. Authentication will occur after Apply or OK is clicked.
A separate window will open allowing the user to login to Microsoft 365 with their username and password and their MFA token (of required). This action will store an authentication cookie from Microsoft 365 in Edge Webview, which is a browser cache storage location.
Users will be prompted to login again when their password changes, or the authentication cookie expires.
How exactly does DMSforLegal (and other products) work with Browser Authentication?
- In DMSforLegal a site connection is created, the Site (URL) is the location to which DMSforLegal will redirect the authentication request
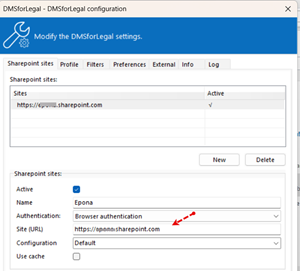
The Edge browser is used to show the webpage of the URL, when authentication is required, the user will be prompted to provide the username and password
Each time the Edge webpage is changed, an event is triggered to DMSforLegal and DMSforLegal will try to capture the two authentication cookies (FedAuth and rtFa)
When the cookies have been retrieved the Browser form is closed by DMSforLegal
If the cookies are invalid or they do not provide access, the Browser form is presented again, untill valid cookies are found. The cookie information is saved by the Edge browser in Webview profile space
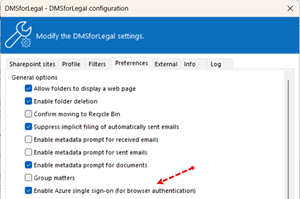
Remark: the Preference *Enable Azure single sign-on (for browser authentication) is switched on by default. If single sign-on provides an authentication token, Browser authentication will use this token. If you switch this preference off, you could logoff in DMSforLegal forcefully.
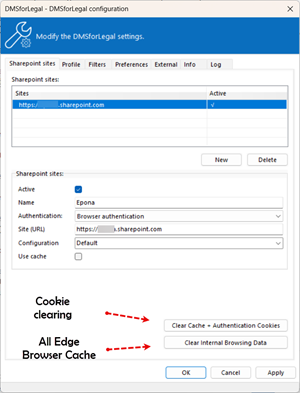
- The Clear Cache button will clear Edge browser cache. This is the cache part in the DMSforLegal Edge Webview profile, not all the cookies.
- The Clear Internal Browsing Data will clear the DMSforLegal Webview Edge cache.
# Other authentication
# Windows Authentication
(Typically used for on-premises SharePoint environments.)
# Username and Password
(Typically used for on-premises SharePoint environments. Legacy/Basic Authentication)
# Multi-factor Authentication
(Sometimes required for external multi-factor authentication protocols when Modern Authentication is not feasible. This feature is deprecated, should not be used)